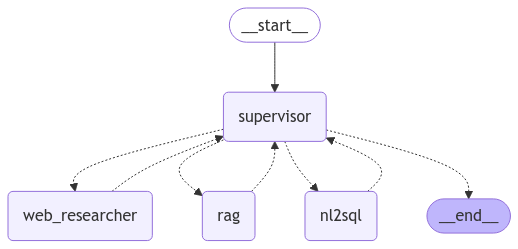
LangSmith News: The Definitive Guide to Building and Monitoring Production-Ready LLM Applications
The landscape of artificial intelligence is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the power and accessibility of Large Language Models (LLMs). Developers are rapidly moving beyond simple chatbot prototypes to build complex, multi-step applications that leverage agents, tools, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). However, this complexity introduces significant engineering challenges. How do you debug a system where the output is non-deterministic? How do you evaluate performance when “correctness” is subjective? How do you monitor cost, latency, and quality in production? This is where LangSmith enters the picture, emerging as an indispensable platform for the LLM-powered application stack. It provides the critical observability, debugging, and evaluation tools needed to transform experimental AI projects into robust, production-grade software. This article offers a comprehensive deep dive into LangSmith, exploring its core features, practical implementation, advanced techniques, and best practices for anyone serious about building reliable applications with LLMs.
Understanding LangSmith: The Observability Layer for LLMs
At its core, LangSmith is a platform designed to help you trace, monitor, and evaluate your language model applications. It acts as a centralized hub for understanding everything that happens inside your LLM chains and agents. While traditional software has well-established observability tools, the unique nature of LLM applications—with their probabilistic outputs and complex, often invisible, intermediate steps—requires a specialized solution. LangSmith fills this gap, providing clarity in a domain that can often feel like a black box. This is a key piece of recent LangChain News, as the platform matures to support the entire lifecycle of LLM app development.
Tracing: The Foundation of Debugging
The most fundamental feature of LangSmith is tracing. Every time your application runs, LangSmith captures a detailed, hierarchical log of the entire execution flow. This isn’t just the final output; it’s every single step along the way. You can see the exact prompt sent to the LLM, the raw output received, the documents retrieved from your vector database, the decisions an agent made, and the inputs and outputs of any tools it used. Each step is logged with crucial metadata like latency and token counts, allowing you to pinpoint performance bottlenecks and unexpected costs instantly. To enable tracing, you simply need to set a few environment variables in your project.
# First, install the necessary libraries
# pip install langchain langchain-openai
import os
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# Set LangSmith environment variables to enable tracing
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_LANGSMITH_API_KEY"
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "My First Project" # Optional: "default" is used if not set
# Set your OpenAI API key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"
# 1. Define a simple chain
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a short joke about {topic}")
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
# 2. Invoke the chain
# This run will automatically be traced in your LangSmith project
response = chain.invoke({{"topic": "machine learning"}})
print(response)Datasets & Evaluation: Ensuring Quality and Performance
Debugging is only half the battle. How do you know if your application is actually getting better? LangSmith’s evaluation capabilities are designed to answer this question. You can create “datasets” of examples, which are essentially collections of inputs and, optionally, reference outputs. You can then run your LLM application over this dataset and apply “evaluators” to score the results. LangSmith provides a suite of built-in evaluators for common tasks (e.g., Q&A correctness, relevance, helpfulness) and also allows you to define your own custom evaluators in Python. This systematic approach allows you to benchmark changes to your prompts, models, or retrieval strategies with concrete metrics, moving beyond anecdotal evidence to data-driven development.

Getting Hands-On: A Practical Guide to LangSmith Integration
Integrating LangSmith is straightforward, especially when using frameworks like LangChain. Let’s build a more complex example—a simple RAG system—to see how LangSmith provides visibility into each component. This system will use a vector store to retrieve relevant information before passing it to an LLM to generate an answer. This is a common pattern where tracing becomes invaluable for diagnosing issues with either the retrieval or the generation step.
Setting Up a RAG Application with Full Tracing
In this example, we’ll use Chroma News favorite, the Chroma vector store, and a simple retriever. When you run this code with the LangSmith environment variables set, you will see a trace that contains distinct steps for retrieval, document formatting, prompt creation, and the final LLM call. This level of detail is crucial for understanding why your RAG system might be providing a suboptimal answer—perhaps it’s retrieving irrelevant documents, or the LLM is ignoring the provided context.
# Install additional libraries
# pip install langchain-community chromadb
import os
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# Ensure LangSmith and OpenAI environment variables are set as before
# os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
# os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_LANGSMITH_API_KEY"
# os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "RAG Analysis"
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"
# 1. Create a simple vector store
documents = ["The Eiffel Tower is in Paris, France.", "The Great Wall of China is a series of fortifications.", "Photosynthesis is the process used by plants to convert light energy into chemical energy."]
vectorstore = Chroma.from_texts(documents, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings())
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={{"k": 1}})
# 2. Define the RAG chain
template = """Answer the question based only on the following context:
{context}
Question: {question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
rag_chain = (
{{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}}
| prompt
| model
| StrOutputParser()
)
# 3. Invoke the chain
# The trace in LangSmith will show the retriever call and the LLM call separately
question = "Where is the Eiffel Tower located?"
response = rag_chain.invoke(question)
print(f"Question: {question}")
print(f"Answer: {response}")Creating and Running Evaluations Programmatically
Now, let’s automate the evaluation of our RAG chain. We’ll create a dataset in LangSmith with a few questions and their ground-truth answers. Then, we’ll use the LangSmith SDK to run our `rag_chain` over this dataset and see the results directly in the UI. This workflow is central to continuous improvement and regression testing for your LLM applications.
# Install the LangSmith SDK
# pip install langsmith
from langsmith import Client
from langchain.evaluation import run_evaluator, EvaluatorType
# 1. Initialize the LangSmith client
client = Client()
# 2. Define a dataset
dataset_name = "RAG QA Dataset"
if not client.has_dataset(dataset_name=dataset_name):
dataset = client.create_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
description="A simple Q&A dataset for our RAG chain."
)
client.create_examples(
inputs=[
{{"question": "Where is the Eiffel Tower located?"}},
{{"question": "What is photosynthesis?"}}
],
outputs=[
{{"answer": "Paris, France"}},
{{"answer": "A process used by plants to convert light energy into chemical energy."}}
],
dataset_id=dataset.id,
)
# 3. Run an evaluation
# This will run the `rag_chain` on each input in the dataset and apply a Q&A evaluator
# The evaluator checks if the generated output is consistent with the reference answer
test_results = client.run_on_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
llm_or_chain_factory=rag_chain,
evaluation={
"evaluators": [EvaluatorType.QA], # Use a built-in Q&A correctness evaluator
"custom_evaluators": [],
},
project_name="RAG Evaluation Run - v1",
# The input to the chain is the 'question' from the dataset
input_mapper=lambda x: x["question"],
)
print("Evaluation complete. Check the results in your LangSmith project.")Beyond Debugging: Advanced LangSmith Features for Production
As your applications move toward production, your needs evolve from simple debugging to sophisticated monitoring, A/B testing, and user feedback analysis. LangSmith provides a suite of advanced features to manage this lifecycle, ensuring your application remains performant and reliable at scale. This is where it complements other MLOps tools like MLflow News favorite MLflow or Weights & Biases News leader Weights & Biases, by focusing specifically on the LLM observability niche.
Customizing Traces with Metadata and Tags
In a production environment, you need to be able to slice and dice your data. You might want to see all the traces for a specific user, a particular session, or from a certain version of your application. LangSmith allows you to add arbitrary metadata and tags to your runs. This is a powerful feature for filtering and analysis. For example, you can tag runs with a `user_id`, `conversation_id`, or `environment` (‘dev’, ‘staging’, ‘prod’) to easily isolate and debug issues reported by a specific customer or occurring in a specific context.
# Building on the previous RAG chain example
import uuid
# Let's simulate a request from a specific user in a production environment
user_id = "user_abc_123"
conversation_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
# Add metadata and tags to the invocation config
response = rag_chain.invoke(
"What is the capital of France?",
config={
"metadata": {
"user_id": user_id,
"conversation_id": conversation_id,
"app_version": "2.1.4",
},
"tags": ["rag", "production", "user-query"],
}
)
print(response)
# In the LangSmith UI, you can now filter runs by tags like 'production'
# or by metadata keys like 'user_id'.Monitoring, Analytics, and User Feedback
LangSmith provides monitoring dashboards that give you a high-level view of your application’s health. You can track key metrics over time, such as P99 latency, cost per run, error rates, and average feedback scores. One of the most critical features for closing the development loop is the ability to log user feedback. When a user indicates whether a response was good or bad (e.g., via a thumbs-up/down button), you can programmatically log this feedback to the corresponding trace in LangSmith. This creates a powerful dataset of real-world successes and failures, which can be used to fine-tune models, improve prompts, or curate high-quality evaluation sets.
from langsmith import Client
client = Client()
# Assume you have the run_id from a previous chain invocation
# In a real app (e.g., using FastAPI or Streamlit), you would store this ID
# For this example, let's get the ID from the last run
last_run = next(client.list_runs(project_name="RAG Analysis", limit=1))
run_id = last_run.id
print(f"Found last run with ID: {run_id}")
# Simulate a user giving a "thumbs up" (a score of 1)
# You can define your own scoring system (e.g., 0 for bad, 1 for good)
client.create_feedback(
run_id=run_id,
key="user_rating", # A key for the feedback type
score=1, # The score given by the user
comment="This answer was very helpful and accurate!"
)
# Simulate a "thumbs down" on another run with a different key
client.create_feedback(
run_id=run_id,
key="correctness",
score=0, # 0 for incorrect
comment="The information was outdated."
)
print(f"Feedback logged for run {run_id}. You can now filter by feedback in the UI.")Best Practices for Production-Grade LLM Observability
Effectively using a tool like LangSmith involves more than just setting environment variables. Adopting a few best practices can dramatically improve your team’s ability to build and maintain high-quality LLM applications.
Structuring Projects and Naming Conventions
Use distinct LangSmith projects for different applications and environments. A common pattern is to have projects like `my-app-dev`, `my-app-staging`, and `my-app-prod`. This separation keeps your data clean and makes it easy to compare performance across environments. Additionally, give your chains, tools, and runnables meaningful names using the `.with_config({“run_name”: “MyCoolStep”})` method in LangChain. This makes your traces much easier to read and understand at a glance.
Integrating with the Modern AI Stack
LangSmith is not an island; it’s a component in a larger ecosystem. It integrates seamlessly with a wide array of tools. Whether you’re getting your models from OpenAI News, Anthropic News, or using open-source models via Hugging Face News, LangSmith can trace the interactions. It works with vector stores from providers mentioned in Pinecone News or Weaviate News. When you deploy your application using FastAPI News or build a demo with Streamlit News, LangSmith continues to provide value by tracing every request. This interoperability is key to its strength.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Not Logging Metadata: Failing to log contextual metadata like `user_id` or `session_id` is a missed opportunity. When a bug is reported, this metadata is often the fastest way to find the exact trace that caused the problem.
- Ignoring Evaluation: Relying on “vibe checks” to see if your app is improving is not scalable. Set up evaluation datasets early and run them regularly to catch regressions and validate improvements.
- Overlooking Cost and Latency: It’s easy to focus only on output quality. Use the LangSmith dashboards to actively monitor token consumption and response times. A slow or expensive application is unlikely to succeed in production, no matter how smart it is.
Conclusion: The Future is Observable
The era of building LLM applications without a dedicated observability strategy is coming to an end. As systems become more complex, incorporating agents, multiple tools, and dynamic retrieval, the need for a tool like LangSmith becomes non-negotiable. It provides the essential trifecta for production readiness: deep tracing for unparalleled debuggability, a robust evaluation framework for ensuring quality and performance, and comprehensive monitoring for maintaining reliability and cost-effectiveness. By integrating LangSmith into your development workflow, you are not just adding a tool; you are adopting a disciplined engineering practice that will allow you to build more sophisticated, reliable, and intelligent applications with confidence. The next wave of innovation, including open, customizable AI platforms, will be built on this foundation of observability.