Build an AI News Summarizer with Streamlit, Groq, and LangChain: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction: Taming the Information Deluge with AI
In today’s hyper-connected world, we are constantly bombarded with news from countless sources. Keeping up with the latest developments in technology, finance, or any field of interest can feel like drinking from a firehose. The sheer volume of information makes it nearly impossible to stay informed without dedicating hours to sifting through articles. This is where the power of Artificial Intelligence, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs), can be a game-changer. By leveraging AI, we can build tools that automatically search, analyze, and summarize vast amounts of text into concise, digestible insights.
This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to building your own AI-powered news summarizer. We will create a user-friendly web application using a modern, efficient technology stack: Streamlit for the interactive front-end, Groq for its blazing-fast LLM inference, the Tavily API for intelligent, AI-optimized web searches, and LangChain to orchestrate the entire workflow. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a functional application that can fetch real-time news on any topic and provide a coherent summary, complete with source links. This project is an excellent entry point into the world of applied AI and demonstrates how quickly you can build powerful tools, a frequent topic in the latest Streamlit News and AI development circles.
Understanding the Core Components
Before diving into the code, it’s essential to understand the role each component plays in our application. This combination of specialized tools allows us to build a robust and responsive application with minimal boilerplate code, a significant advantage over building from scratch with frameworks like Flask News or FastAPI News.
Streamlit: The Pythonic Way to Build Web Apps
Streamlit is an open-source Python library that makes it incredibly simple to create and share beautiful, custom web apps for machine learning and data science. Its core philosophy is to turn data scripts into shareable web apps in minutes. You write standard Python code, and Streamlit handles the complexities of rendering a front-end, managing state, and creating interactive widgets. This is why it has become a favorite for rapid prototyping in the AI community, often featured alongside updates in Gradio News and Chainlit News.
Here’s a simple “Hello, World!” example to illustrate its simplicity:
import streamlit as st
# Set the title of the app
st.title("My First Streamlit App")
# Display a simple text message
st.write("Hello, world! Welcome to interactive Python apps.")
# Add an interactive text input widget
name = st.text_input("What's your name?")
# Conditionally display a personalized greeting
if name:
st.write(f"Hello, {name}!")Groq: Blazing-Fast LLM Inference
The “brain” of our summarizer is the LLM. While there are many providers, from the subjects of OpenAI News and Anthropic News to platforms like Google DeepMind News, we’re using Groq. Groq has made a name for itself by providing astonishingly fast inference speeds for open-source models like Llama 3 and Mixtral. This speed is achieved through their custom-built Language Processing Units (LPUs), which are designed specifically for sequential processing tasks inherent to LLMs. For an interactive application like a news summarizer, low latency is critical for a good user experience, making Groq an excellent choice.
Tavily AI: Your Intelligent Search Agent
To summarize the news, we first need to find it. A standard search engine API might return a list of links and snippets, but this raw data often requires significant cleaning and processing. Tavily AI is a search API built specifically for LLMs and AI agents. It scours the web and returns clean, relevant, and context-rich information, abstracting away the need for web scraping and content extraction. This allows our LangChain agent to focus on the core task of summarization rather than data wrangling.
LangChain: The Orchestration Engine
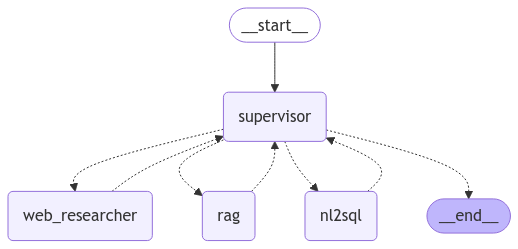
The latest LangChain News consistently highlights its role as the premier framework for developing applications powered by LLMs. It acts as the glue that connects our components. LangChain provides a standardized interface for interacting with LLMs (like the one from Groq), tools (like the Tavily search), and prompts. We will use it to build an “agent”—an autonomous entity that uses the LLM to reason about which tools to use and how to sequence actions to accomplish a goal. This agent-based approach is powerful and flexible, allowing for more complex workflows than a simple prompt-and-response cycle.
Building the AI News Summarizer: A Practical Walkthrough
Streamlit LangChain Groq logos – Create a SQL Agent using CrewAI and Groq | by Plaban Nayak | The …
Now, let’s get our hands dirty and build the application. We’ll start with setting up the environment and then progressively add the UI and the core AI logic.
Setting Up Your Environment
First, you’ll need to install the necessary Python libraries. It’s highly recommended to do this within a virtual environment.
pip install streamlit python-dotenv langchain langchain-groq langchain_community tavily-pythonNext, you need to obtain API keys from both Groq and Tavily AI. For local development, the best practice is to store these keys in a .env file in your project’s root directory:
.env file:
GROQ_API_KEY="gsk_..."
TAVILY_API_KEY="tvly-..."We’ll use the dotenv library to load these into our environment when the script runs.
Creating the Basic Streamlit UI
Let’s create a file named app.py and lay out the basic user interface. We need a title, a text input box for the user to enter a news topic, and a button to trigger the process.
import streamlit as st
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# Load environment variables from .env file
load_dotenv()
# Set up the Streamlit page configuration
st.set_page_config(page_title="AI News Summarizer", layout="wide")
st.title("⚡ AI-Powered News Summarizer")
st.markdown("<p>Enter a topic below to get a real-time summary of the latest news, powered by Groq, Tavily, and LangChain.</p>", unsafe_allow_html=True)
# Input field for the user to enter a news topic
topic = st.text_input("Enter a news topic to summarize:", "Latest updates from Meta AI News")
# Button to trigger the summarization
summarize_button = st.button("Summarize News", type="primary")
# Placeholder for the results
if summarize_button and topic:
if not os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY") or not os.getenv("TAVILY_API_KEY"):
st.error("API keys not found. Please set them in a .env file.")
else:
with st.spinner(f"Searching and summarizing news about '{topic}'..."):
# This is where our main AI logic will go
st.success("Summarization complete!")
st.write("The summary will appear here.")Integrating LangChain for Search and Summarization
Now, we’ll implement the core logic inside the button’s conditional block. We will initialize the Groq LLM and the Tavily search tool, then combine them into a LangChain agent that can reason and act.
import streamlit as st
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain_groq import ChatGroq
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_tool_calling_agent
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
# --- Streamlit UI (as defined previously) ---
st.set_page_config(page_title="AI News Summarizer", layout="wide")
st.title("⚡ AI-Powered News Summarizer")
topic = st.text_input("Enter a news topic to summarize:", "Latest in Hugging Face News")
summarize_button = st.button("Summarize News", type="primary")
# --- Main Logic ---
if summarize_button and topic:
if not os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY") or not os.getenv("TAVILY_API_KEY"):
st.error("API keys not found. Please set them in a .env file.")
else:
with st.spinner(f"Unearthing the latest on '{topic}'..."):
try:
# 1. Initialize the LLM for fast inference
llm = ChatGroq(model="llama3-8b-8192", temperature=0.2)
# 2. Create the Tavily search tool
# max_results=5 ensures we get a good breadth of sources
search_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=5)
tools = [search_tool]
# 3. Define the agent's prompt template
# This guides the LLM on its role, inputs, and expected output format.
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a world-class news reporter and summarizer. Your goal is to provide a clear, concise, and unbiased summary of the provided search results. You must include the source URLs for the information you present."),
("human", "{input}"),
("placeholder", "{agent_scratchpad}"),
])
# 4. Create the agent
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True)
# 5. Invoke the agent and stream the output
full_query = f"Provide a comprehensive summary of the latest news about {topic}. The summary should be well-structured, easy to read, and cover the key points from multiple sources. Include the source URLs as markdown links."
response = agent_executor.invoke({"input": full_query})
st.success("Summary Generated!")
st.markdown(response["output"])
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"An error occurred: {e}")To run your app, save the code as app.py and execute streamlit run app.py in your terminal. You now have a working AI news summarizer!
Taking It to the Next Level: Advanced Features
A basic summarizer is great, but we can add more features to make it more powerful and user-friendly. These enhancements also provide opportunities to explore more of the AI and MLOps ecosystem, including tools often discussed in MLflow News or platforms like AWS SageMaker News.
Adding Model and Parameter Selection
Let’s give the user more control by allowing them to select the LLM model and adjust its “temperature” (a parameter that controls the randomness of the output). We can add these widgets to a sidebar.

Streamlit LangChain Groq logos – Build A Local Reliable RAG Agent Using CrewAI And Groq | by Plaban …
In your app.py, add the following to create a sidebar:
with st.sidebar:
st.header("Configuration")
selected_model = st.selectbox(
"Choose a model",
["llama3-8b-8192", "llama3-70b-8192", "mixtral-8x7b-32768"],
index=0
)
temperature = st.slider(
"Set temperature",
min_value=0.0, max_value=1.0, value=0.2, step=0.1
)
Then, modify the LLM initialization to use these values: llm = ChatGroq(model=selected_model, temperature=temperature). This modularity is key; you could easily extend this to use models from Azure AI News or Amazon Bedrock News by swapping out the `ChatGroq` class.
Caching for Performance and Cost Savings
LLM API calls can be slow and costly. If multiple users ask for a summary of the same topic within a short period, we shouldn’t have to re-run the entire process. Streamlit’s caching decorators are perfect for this. We can wrap our agent execution logic in a cached function.
# (Place this function definition at the top of your script)
@st.cache_data(show_spinner=False, ttl=1800) # Cache results for 30 minutes
def get_summary(query: str, model_name: str, temp: float):
"""
A cached function to perform the search and summarization.
Streamlit's caching hashes the input arguments to decide whether to re-run.
"""
print(f"CACHE MISS: Running agent for query: {query}") # This will print to console on a cache miss
llm = ChatGroq(model=model_name, temperature=temp)
search_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=5)
tools = [search_tool]
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a professional news summarizer. Provide a concise, well-structured summary of the search results, including source URLs as markdown links."),
("human", "{input}"),
("placeholder", "{agent_scratchpad}"),
])
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools)
full_query = f"Provide a comprehensive summary of the latest news about {query}."
response = agent_executor.invoke({"input": full_query})
return response["output"]
# --- In the main logic block ---
if summarize_button and topic:
with st.spinner(f"Generating summary for '{topic}'..."):
summary_output = get_summary(topic, selected_model, temperature)
st.success("Summary Generated!")
st.markdown(summary_output)Expanding to a RAG System with Vector Stores
Our current app is a simple “Search-then-Summarize” agent. A more advanced architecture is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Instead of just summarizing live results, you could build a system that continuously ingests news articles, chunks them into smaller pieces, converts them to numerical representations (embeddings) using a library like those from Sentence Transformers News, and stores them in a specialized vector database. Popular choices often seen in Pinecone News, Chroma News, or Weaviate News allow for efficient similarity search. Your app could then query this internal knowledge base to provide summaries based on a curated set of articles, offering more control and consistency.
Best Practices and Optimization
Building a functional prototype is the first step. To create a truly great application, consider these best practices.
Prompt Engineering and Debugging
The quality of your summary is highly dependent on your prompt. Be explicit about the desired tone, format, and length. Experiment with different phrasings. For complex chains, debugging can be difficult. Tools like those featured in LangSmith News are invaluable for tracing the execution of your LangChain agents, allowing you to see exactly what the LLM is thinking and which tools it’s using.
UI/UX and Performance
A good user experience is paramount. Always use `st.spinner` to give feedback during long-running operations. Organize complex interfaces with `st.tabs` or `st.columns`. For resource-intensive tasks, you might consider offloading work to a background job system. If you decide to self-host models for more control over performance and cost, using inference servers like Triton Inference Server News or frameworks like vLLM News on platforms such as Modal News or RunPod News can dramatically improve throughput, especially when optimized with tools like TensorRT News.
Deployment and Scaling
Once your app is ready, you can easily deploy it using Streamlit Community Cloud for free. For more demanding applications, you can containerize it with Docker and deploy it on any major cloud provider. As your app scales, you might explore distributed computing frameworks like those in Ray News or Dask News to handle larger data processing pipelines, perhaps running on a platform like Vertex AI News or Azure Machine Learning News.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In this article, we have successfully built a powerful and interactive AI news summarizer. We’ve seen how modern tools like Streamlit, Groq, Tavily, and LangChain can be combined to rapidly prototype and develop sophisticated AI applications. The key takeaway is the power of composition: by connecting specialized, best-in-class services, we can achieve results that would have required a large team and months of effort just a few years ago.
The journey doesn’t end here. You can extend this application in numerous ways. Consider adding historical trend analysis, sentiment analysis for each news topic, or translating summaries into different languages. You could also explore alternative frameworks like those from LlamaIndex News for building RAG pipelines or experiment with locally-run models using Ollama News. The ecosystem of AI tools is constantly evolving, with exciting developments in PyTorch News and Tensor