Leveraging IBM Watson News for Advanced AI: A Developer’s Guide to Real-Time Insights
In today’s hyper-connected world, the sheer volume of global news generated every second is staggering. For developers and data scientists, this torrent of information represents both a monumental challenge and an unprecedented opportunity. Sifting through this data to find relevant signals, understand market sentiment, or track emerging trends is a task far beyond manual human capability. This is where AI-powered news intelligence platforms come into play. Among the most powerful is IBM Watson News, a service that provides a continuously updated, pre-enriched stream of news data from tens of thousands of global sources. It transforms raw text into a structured, queryable resource, complete with identified entities, concepts, keywords, and sentiment analysis.
This article provides a comprehensive technical guide for developers looking to harness the power of IBM Watson News. We will move beyond a simple overview and dive deep into practical implementation, showing you how to integrate this rich data source into sophisticated AI applications. We’ll explore how to build a news-aware Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system using frameworks like LangChain, analyze trends over time, and connect Watson’s capabilities to the broader AI ecosystem, including models from OpenAI News, Anthropic News, and deployment platforms like AWS SageMaker News and Azure AI News. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and code examples to start building your own intelligent, news-driven applications.
The Anatomy of Enriched News Data
Before building applications, it’s crucial to understand the foundational elements of IBM Watson News. It’s not just a news aggregator; it’s a component of the larger IBM Watson Discovery service, which applies Natural Language Processing (NLP) to enrich unstructured data. This enrichment process is what turns a simple news article into a valuable asset for machine learning.
What is IBM Watson Discovery News?
IBM Watson Discovery News is a pre-built data collection within the Watson Discovery service that is constantly updated with articles from reputable news outlets worldwide. When an article is ingested, it undergoes a series of NLP enrichments, which are then stored as metadata alongside the original text. Key enrichments include:
- Entities: Identification of people, companies, organizations, and locations (e.g., “NVIDIA,” “Jensen Huang,” “California”).
- Concepts: High-level concepts the article discusses (e.g., “Artificial Intelligence,” “Semiconductors,” “Machine Learning”).
- Keywords: Important terms and phrases that are central to the article’s topic.
- Categories: A hierarchical taxonomy classifying the article (e.g., /technology and computing/artificial intelligence).
- Sentiment: A document-level sentiment score (positive, neutral, negative) and target-level sentiment for specific keywords or entities.
- Relations: The semantic relationships between identified entities (e.g., “Elon Musk” – “CEO of” – “Tesla”).
This structured data allows for highly specific and powerful queries that are impossible with traditional search engines, forming a solid foundation for insights that can power everything from financial analysis tools to brand reputation monitors.
Accessing the Data: The Watson Discovery API
Interaction with Watson News is done via the Watson Discovery API, which is accessible through the IBM Cloud. To get started, you’ll need an IBM Cloud account and a provisioned Watson Discovery instance, from which you can obtain your API Key and Service URL.
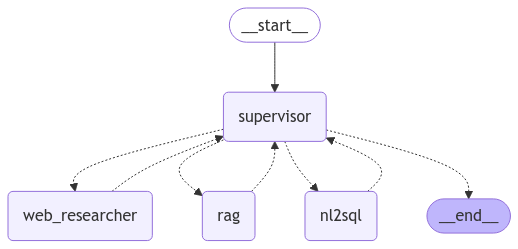
The primary way to interact with the service in Python is through the ibm-watson SDK. Here’s a basic example of how to perform a query to find recent articles mentioning a specific company, such as the latest NVIDIA AI News.
# First, install the SDK: pip install ibm-watson
import json
from ibm_watson import DiscoveryV2
from ibm_cloud_sdk_core.authenticators import CloudPakForDataAuthenticator, IAMAuthenticator
# --- Authentication ---
# Use IAMAuthenticator for IBM Cloud instances
authenticator = IAMAuthenticator('YOUR_API_KEY')
discovery = DiscoveryV2(
version='2020-08-30',
authenticator=authenticator
)
discovery.set_service_url('YOUR_SERVICE_URL')
# --- Configuration ---
PROJECT_ID = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID' # The project ID for your Discovery instance
# Note: For the built-in Watson News collection, you often use a pre-configured project.
# You can find the Project ID in your IBM Cloud Discovery service dashboard.
# --- Query ---
# Let's search for articles about NVIDIA's recent developments in AI
query_result = discovery.query(
project_id=PROJECT_ID,
query='enriched_text.entities.text:"NVIDIA" AND "artificial intelligence"',
count=5 # Get the top 5 results
).get_result()
# --- Process Results ---
print(json.dumps(query_result, indent=2))
# Extracting specific information
print("\n--- Found Articles ---")
for result in query_result.get('results', []):
title = result.get('title', 'No Title')
url = result.get('url', 'No URL')
print(f"Title: {title}\nURL: {url}\n")This simple script demonstrates the core workflow: authenticate, define a project, execute a query using the Discovery Query Language (DQL), and parse the resulting JSON. The real power lies in crafting more complex DQL queries to filter by date, sentiment, categories, and more.
Practical Implementation: Building a News-Aware RAG Pipeline
One of the most powerful applications of real-time news data is in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). RAG systems enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by providing them with external, up-to-date information, grounding their responses in facts and reducing hallucinations. Using IBM Watson News as the retrieval source ensures your LLM has access to vetted, current events.
Why RAG for News Analysis?
LLMs from providers like OpenAI News or Google DeepMind News are trained on vast but static datasets. Their knowledge has a cutoff date, making them unreliable for questions about recent events. A RAG pipeline solves this by first retrieving relevant documents (from Watson News) and then passing that context to the LLM along with the user’s query. Frameworks like LangChain News and LlamaIndex News have made building these pipelines more accessible than ever.
Step 1: Data Ingestion and Indexing
The first step is to fetch relevant articles from Watson News and prepare them for a vector database. This involves querying, extracting text, and splitting the text into manageable chunks. For storage and efficient retrieval, we’ll use a vector database like Pinecone News, Weaviate News, or an open-source library like FAISS News or Chroma News.
# Prereqs: pip install ibm-watson langchain sentence-transformers
from ibm_watson import DiscoveryV2
from ibm_cloud_sdk_core.authenticators import IAMAuthenticator
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
def fetch_and_chunk_articles(api_key, service_url, project_id, query, num_articles=10):
"""
Fetches articles from Watson News and splits them into text chunks.
"""
authenticator = IAMAuthenticator(api_key)
discovery = DiscoveryV2(version='2020-08-30', authenticator=authenticator)
discovery.set_service_url(service_url)
# Use DQL to find recent, relevant articles in English
full_query = f"language:en,({query})"
query_result = discovery.query(
project_id=project_id,
query=full_query,
count=num_articles
).get_result()
documents = []
for result in query_result.get('results', []):
# We use the main text content for our RAG context
text = result.get('text', '')
if text:
documents.append({
"text": text,
"metadata": {
"source": result.get('url', 'N/A'),
"title": result.get('title', 'N/A')
}
})
# Initialize a text splitter from LangChain
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=150,
length_function=len
)
all_chunks = []
for doc in documents:
chunks = text_splitter.split_text(doc['text'])
for chunk in chunks:
all_chunks.append({"page_content": chunk, "metadata": doc['metadata']})
return all_chunks
# --- Example Usage ---
API_KEY = 'YOUR_API_KEY'
SERVICE_URL = 'YOUR_SERVICE_URL'
PROJECT_ID = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
# Let's get news about advancements in PyTorch and TensorFlow
search_query = 'enriched_text.concepts.text:"PyTorch" OR enriched_text.concepts.text:"TensorFlow"'
chunked_documents = fetch_and_chunk_articles(API_KEY, SERVICE_URL, PROJECT_ID, search_query)
print(f"Fetched and chunked {len(chunked_documents)} documents.")
print("--- Sample Chunk ---")
print(chunked_documents[0])Step 2: Embedding and Retrieval
Once we have our text chunks, we need to convert them into numerical representations (embeddings) that capture their semantic meaning. We can use open-source models from Hugging Face Transformers News via the Sentence Transformers News library or API-based models from Cohere News. These embeddings are then stored in our vector database for fast similarity searches.

# Prereqs: pip install langchain sentence-transformers faiss-cpu
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
# This assumes 'chunked_documents' is available from the previous step
# 1. Initialize an embedding model from Hugging Face
# Using a popular, high-performance model
model_name = "sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
# You can use GPU-enabled containers on platforms like RunPod or Modal for faster inference
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name=model_name)
# 2. Extract just the page_content for embedding
page_contents = [doc['page_content'] for doc in chunked_documents]
metadatas = [doc['metadata'] for doc in chunked_documents]
# 3. Create the FAISS vector store from the documents and embeddings
# This process can be tracked using MLOps tools like MLflow News or Weights & Biases News
print("Creating FAISS vector store... This may take a moment.")
vector_store = FAISS.from_texts(texts=page_contents, embedding=embeddings, metadatas=metadatas)
print("Vector store created successfully.")
# 4. Now we can perform a similarity search
user_question = "What are the latest performance optimizations in PyTorch 2.0?"
retrieved_docs = vector_store.similarity_search(user_question, k=3)
# The retrieved_docs now contain the most relevant chunks from the news articles
print(f"\n--- Top 3 relevant chunks for the question: '{user_question}' ---")
for doc in retrieved_docs:
print(f"Source: {doc.metadata['source']}")
print(f"Content: {doc.page_content[:250]}...\n")
# This 'vector_store' object can now be integrated into a full LangChain RAG chain.Advanced Techniques: From Trend Analysis to Agentic Workflows
Beyond RAG, the structured data from IBM Watson News enables more advanced analytical applications. By leveraging its time-series and filtering capabilities, you can uncover deeper insights and build more sophisticated AI systems.
Time-Series Trend Analysis
The Watson Discovery API allows you to perform aggregations, which are perfect for tracking trends. You can analyze the frequency of mentions of a specific technology, company, or concept over time, and even break it down by sentiment. This is invaluable for market research, competitive analysis, and understanding public perception.
For example, you could track news volume related to different AI frameworks like PyTorch News, TensorFlow News, or the rapidly growing JAX News ecosystem.
# Prereqs: pip install ibm-watson pandas matplotlib
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ibm_watson import DiscoveryV2
from ibm_cloud_sdk_core.authenticators import IAMAuthenticator
def analyze_trend(api_key, service_url, project_id, keyword):
"""
Analyzes the news frequency of a keyword over the last 30 days.
"""
authenticator = IAMAuthenticator(api_key)
discovery = DiscoveryV2(version='2020-08-30', authenticator=authenticator)
discovery.set_service_url(service_url)
# Build an aggregation query to count documents per day
aggregation_query = f"timeslice(crawl_date,1day).term(enriched_text.keywords.text,count:10)"
filter_query = f"enriched_text.keywords.text:\"{keyword}\""
query_result = discovery.query(
project_id=project_id,
aggregation=aggregation_query,
filter=filter_query,
count=0 # We only care about the aggregation, not the documents
).get_result()
# Process the aggregation results
timeslice_data = query_result['aggregations'][0]['results']
dates = [pd.to_datetime(item['key_as_string'].split('T')[0]) for item in timeslice_data]
counts = [item['matching_results'] for item in timeslice_data]
df = pd.DataFrame({'date': dates, 'mentions': counts}).sort_values('date')
# Plot the results
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(df['date'], df['mentions'], marker='o', linestyle='-')
plt.title(f"Daily News Mentions for '{keyword}' Over the Last 30 Days")
plt.xlabel("Date")
plt.ylabel("Number of Articles")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
# --- Example Usage ---
# Let's track news about "DeepSpeed", a popular library for training large models
analyze_trend(API_KEY, SERVICE_URL, PROJECT_ID, "DeepSpeed")Integrating with AI Agents and Frameworks
Modern AI development is moving towards autonomous agents that can use tools to accomplish complex tasks. You can easily wrap the Watson News API into a custom tool for an agent built with LangChain or Haystack News. This would empower an agent, powered by a model from Mistral AI News or Meta AI News, to perform real-time research. For instance, you could ask the agent: “Summarize the top three news stories about advancements in AI hardware from the past 48 hours.” The agent would use its Watson News tool to fetch the data, then use its language capabilities to synthesize a summary.
Best Practices and Navigating the AI Ecosystem
To effectively use IBM Watson News at scale, it’s important to follow best practices for querying, cost management, and integration with the broader MLOps and cloud-native AI stack.
Query Optimization and Cost Management
- Be Specific: Use the Discovery Query Language (DQL) to its full potential. Filter by entity type (
enriched_text.entities.type::Company), category, and date ranges to narrow your results. This reduces the number of documents processed and lowers costs. - Use Filters, Not Just Queries: The
filterparameter is more efficient for metadata-based filtering than the mainqueryparameter. Usefilterfor known values like dates and categories, andqueryfor natural language text searches. - Cache Results: For applications with recurring queries, implement a caching layer (e.g., using Redis) to avoid repeatedly calling the API for the same information, which saves both time and money.
Integrating with the Modern AI Stack
IBM Watson News is a data source, not an end-to-end platform. Its true value is realized when combined with other leading tools and platforms:
- Cloud Platforms: The applications you build can be deployed and scaled on major cloud providers. You can use Vertex AI News on Google Cloud, AWS SageMaker on AWS, or Azure Machine Learning News to host your models, run your RAG pipelines, and manage your infrastructure.
- MLOps and Experiment Tracking: As you build more complex systems, use tools like MLflow News, Comet ML, or Weights & Biases News to track experiments, log model performance, and manage the lifecycle of your AI applications.
- Data Platforms: For enterprise-grade analytics, you can pipe the data from Watson News into platforms like Snowflake Cortex, where it can be joined with your internal business data for comprehensive insights.
- Interactive Demos: Quickly build and share interactive demos of your news-powered applications using frameworks like Streamlit News, Gradio News, or Dash.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Real-Time News
IBM Watson News offers developers a powerful, structured, and continuously updated firehose of global information. We’ve seen how to move from simple API queries to building sophisticated, real-time AI applications like RAG systems and trend analysis dashboards. By leveraging the rich enrichments provided by Watson, you can build applications that are not only intelligent but also contextually aware and grounded in the latest factual information.
The key takeaway is that this service is a powerful data provider within a larger, vibrant ecosystem. By combining its capabilities with open-source frameworks like LangChain and PyTorch, vector databases like Milvus or Qdrant, and scalable cloud platforms, you can unlock immense value. The next step is to identify a problem or opportunity that can be addressed with real-time news intelligence and start building. The tools are at your disposal to create the next generation of data-driven AI solutions.